

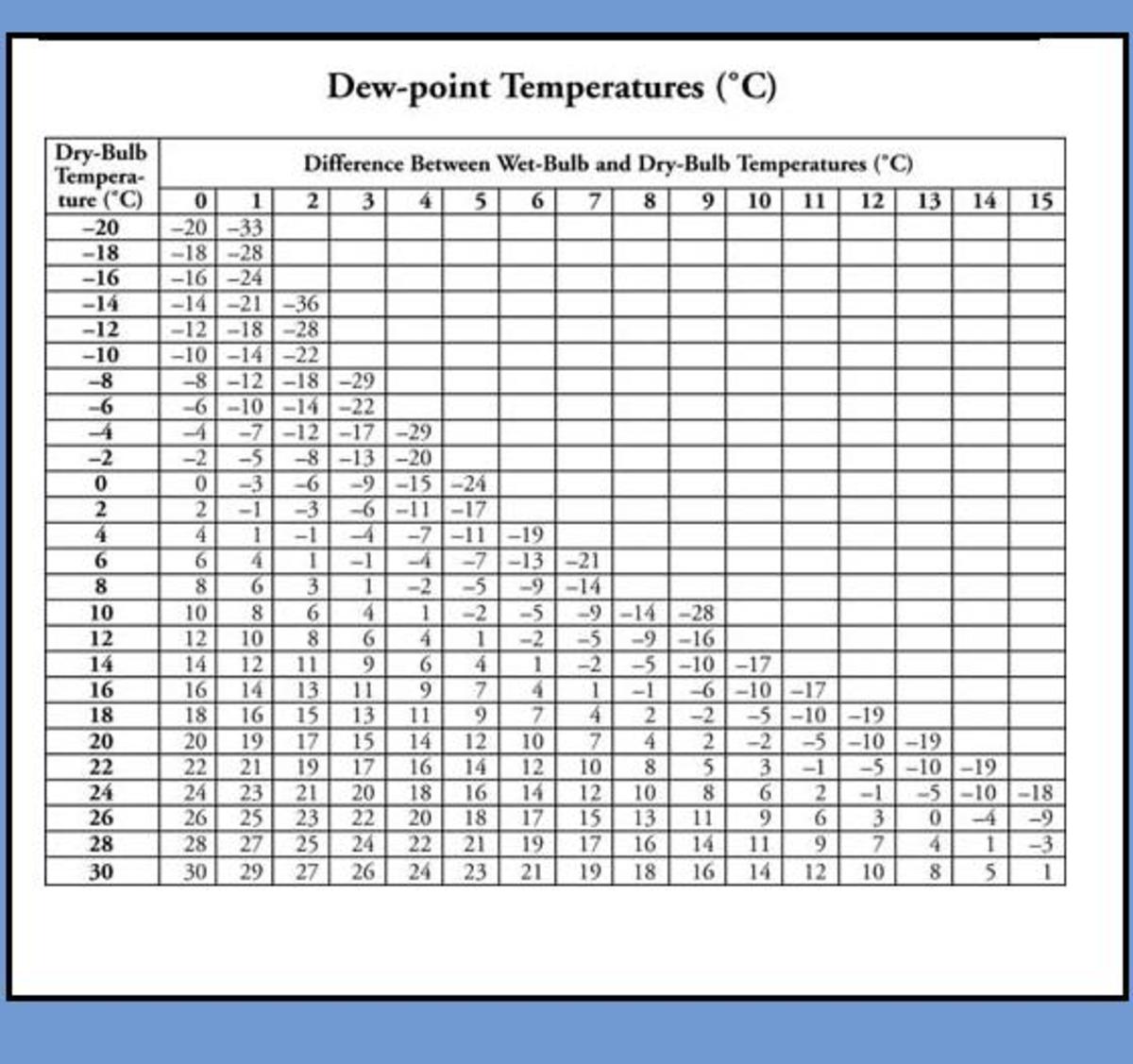
The data: The sample graph below illustrates when the potential for condensation can occur inside a wall cavity with either no or too little exterior insulation.The result: the surface (usually a wall) gets wet, and mold and mildew begin to grow. This means that warm, moist outdoor air can get in, reach a cool surface, and condense. The reality: Many walls have too little insulation and too many air leaks.It will also (hopefully) make the building more comfortable. The perception: When you insulate a wall, it reduces the heating and cooling costs of a building.This example is for a 2×4 wall in climate zone 4* The question then becomes: when does it make sense to add exterior insulation and when can it be skipped? Get in touch today with your question.As energy codes get more stringent, adding exterior wall insulation is becoming a reality for more builders. As well as our standard sampling systems, we can also help with customised products. Our sales engineers are happy to discuss your application and help you find the best solution. Get expert advice for measuring PDP in your application The Michell Easidew Advanced Online Hygrometer is capable of displaying and compensating for live pressure changes with an optional external pressure sensor.
#WATER DEW POINT CALCULATOR PORTABLE#
MDM50 and Easidew Portable include integral sampling systems, while the MDM300 has a separate, optional sampling system. The Michell MDM300, MDM50 and Easidew Portables are also suitable for use at line pressure. All Michell Dew-Point Transmitters are capable of operating in pressures up to 450 barg (6570 psig). Making sure that the dew-point transmitter used is suitable for use at pressure is also important. When sampling at high line pressures, ensuring that the system has been pressure-tested is also important for safety. ‘8 common pitfalls in moisture measurement’ for more information on choosing the right moisture sampling components.

Dead volumes, trapped moisture and choice of materials are all common pitfalls to watch out for – see our article Using the right sample system is essential for accurate moisture measurements.
#WATER DEW POINT CALCULATOR HOW TO#
How to get the best results when measuring water dew point at pressure
The three main applications for measuring PDP are: What are the main applications for measuring pressure dew points? The diagram below illustrates this effect. Eventually, as the pressure increases, the water vapor in the gas will reach its saturation point and will start to condense, despite the temperature remaining the same. Change either one of these parameters and the dew point temperature will alter too.Īs the total pressure of the gas rises, the partial pressures also rise. However, dew point temperature is not fixed – it's related to both the absolute moisture content and the pressure of the gas. If the ambient temperature drops to +6 ☌, then moisture will condense in the line. For example, if the dew point temperature of a compressed air line is +7 ☌ dew point, and the ambient temperature is +20 ☌, there will be no condensation. Condensation occurs when the ambient temperature of the process drops below the dew point temperature of measured gas. How does pressure affect dew point?ĭew-point temperature is a key parameter for avoiding condensation. The pressure difference does not need to be high to affect the dew point temperature: even a change of 1 bar above atmospheric pressure counts as a pressure dew point. Unlike moisture content which is a fixed value no matter the temperature or the pressure, the dew point temperature of a gas is relative to the pressure. Atmospheric dew point is often abbreviated to (ADP). The term ‘pressure dew point’ (PDP) is used when the gas is at a pressure higher than normal atmospheric pressure. In industrial applications, dew point is used as a measurement of humidity in either a process gas or within a controlled environment. This article covers the basic theory behind calculating dew point temperatures at higher than atmospheric pressure and suggests best practices for sampling and measurement techniques.

Many applications use gas or air at pressure so calculating pressure dew-point (PDP) temperature accurately is essential. It can damage equipment, make its way into sensitive processes, shorten the life of air-driven tools or reduce product quality. Avoiding condensation is vital for many processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
